– Magnesium is the most important mineral in the body. It is involved in more than 300 enzyme reactions and in 80% of all metabolic processes in the body, such as ATP synthesis (energy production).
– At least 75- 88% of the population are not getting enough magnesium (state 2010).
– In spite of this, all-in-one-mineral supplements that contain 100% of most essential minerals usually only contain 10- 15 % of the recommended daily value of magnesium.
– Magnesium content in foods has decreased 80 – 90% in the past few decades. So, it is increasingly difficult to get the daily requirement from food. (see Figure nutrient contents below). [1]
– Environmental factors reduce magnesium content in soils and food plants. These factors also reduce magnesium absorption into the body and accelerate magnesium excretion from the body.
– Magnesium deficiency can cause or worsen any chronic disease known to mankind, first and foremost hypertension, heart disease and disorders of the nervous system.
– “Magnesium has a fundamental role in the control of neuronal and vasomotor activities, bone formation, cardiac excitability, neuromuscular transmission, muscle contraction and glucose metabolism.” [2]
Who has magnesium deficiency?
– Dr. Thomas Levy: “if you are on planet earth and alive today, you have low [suboptimal] magnesium levels. “
A diet modelling study based on NHANES 2007-2010 data revealed that the percentage of individuals consuming below the estimated average requirement (EAR) for magnesium ranged from 51.7 % to 88.5% for US adult males. [3]
– The University of Notre Dame gives a lower percentage: “75% of the population are not getting enough magnesium.” [4]
Both assessments were made before the Covid era.
– 96.7% of pregnant women throughout pregnancy are affected by magnesium deficiency. [5]
Symptoms of deficiency
In addition to hypertension, heart disease and disorders of the nervous system, magnesium deficiency can cause inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, constipation, chronic fatigue as well as osteoporosis and migraine headaches.
“Magnesium deficiency usually causes psychiatric symptoms, such as anxiety, insomnia, hyperemotionality, depression, headache, dizziness, and tremors.” [6]
– Further “Low serum magnesium is associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) mortality and sudden cardiac death (SCD).” [7]
Chronic pain
“Chronic pain sufferers consume less magnesium…” [8]
Back pain
“One of the main causes of chronic idiopathic back pain appears to be magnesium deficiency.” [9]
Magnesium is needed to properly metabolize vitamin D. “Low magnesium levels make vitamin D ineffective.” [10]
Depletion in soil, food and the human body:
Historically, bioavailable magnesium used to be plentiful in soil and foods.
“Many fruits and vegetables have lost large amounts of minerals and nutrients in the past 100 years with estimates that vegetables have dropped magnesium levels by 80–90% in the U.S. and the UK. “
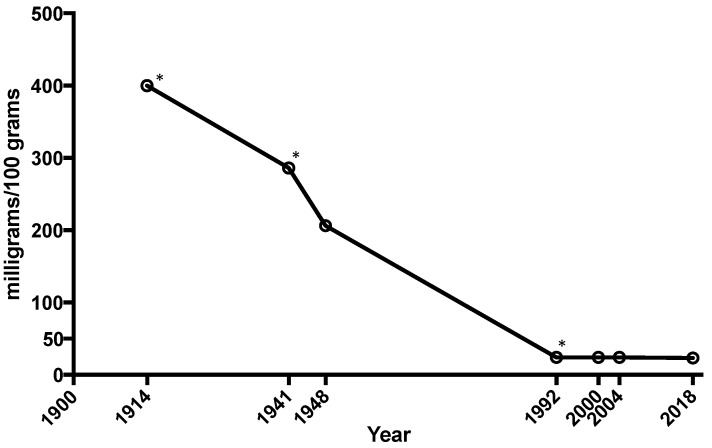
Fig. 1 The average mineral content of calcium, magnesium and iron in cabbage, lettuce, tomatoes and spinach has dropped 80-90% between 1914 and 2018. Workinger JL, Doyle RP, Bortz J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Magnesium Status. Nutrients. 2018; 10(9):1202.
In recent decades, the depletion in soil and food was further accelerated exponentially, and lists of magnesium content in foods are outdated.
For instance, the USDA values as used today for magnesium content in wheat flower (white) were published in 1989 [11], for black beans or tofu it’s 1986, for yogurt it’s 1976. [12] That was at the beginning of the Green Revolution, when all foods were basically organic. Since then, only glyphosate use alone in US agriculture has increased 40-fold. [13]
For other foods: “It is important to note that the USDA mineral content of vegetables and fruits has not been updated since 2000.“ [14]
The data for spinach, listed as one of the most magnesium-rich foods, are from 2002. [15]
Thus, all recommendations of how much of a food source is needed to meet the daily Mg requirements are essentially useless.
Factors that reduce magnesium include:
– Intensive farming, especially with heavy machinery and intensive ploughing have caused wash out of magnesium from soil for a century. With the Green Revolution, chemical fertilizers and acid rain accelerated the process. In recent years the use of GMOs and Glyphosate has brought magnesium content in food to dwindling lows.
– Acid rain, acid soil, “Acid rain induces mobilization and washing out of relatively large amounts of calcium and magnesium even from sandy and naturally very acid soils.” [16]
– Glyphosate (it is allowed even for coating of organic foods) and other pesticides). [17]
“Glyphosate can impede absorption and translocation of calcium and magnesium in Glyphosate plants. [sd1] “ But given the state of depletion of the soil, organic produce contains only 30% more magnesium than conventional produce. [18]
– food processing
“Typical grain refining processes for bread and pasta remove 80-95% of total magnesium.” [19] Generally, food processing leads to magnesium loss of up to 85%. [20]
Factors preventing magnesium absorption from food and accelerating magnesium excretion:
– toxic metals (cadmium, lead, etc.) cause the loss of essential metals (Mg, Ca, etc.) [21]
– saturated and trans fats, non-fermentable fibre (like wheat bran), high sugar intake
– certain antibiotics, blood pressure medication (proton pump inhibitors and diuretics), some antibiotics, [22] many SSRI antidepressants; [23] oxalates, excess calcium and phosphates, (fertilisers, soft drinks)
– ageing, disease and stress
– gastrointestinal diseases
– type 2 diabetes
– certain types of cardiac insufficiencies and kidney disease.
– fluoride
“Fluoride, found in 74% of the American population’s drinking water, with ~50% of drinking water having a concentration of 0.7 mg/L, prevents magnesium absorption through binding and production of insoluble complexes.” [24]
Video: Thomas Levy, MD., Reversing Disease with Magnesium
Highlights:
– “All disease is caused by oxidative stress, which is all that a toxin does.”
– “Even though magnesium is not an antioxidant per se, it is probably the most essential nutrient that exists to sustain a normal intercellular environment and metabolism.”
– Calcium is needed in the body, but almost exclusively outside the cells.
– “All disease (100%) is characterised by, associated with and caused by excess calcium inside the cells that are affected.”
– “Magnesium is natures natural anti calcium agent.”
– “Magnesium directly antagonises most of the metabolic reactions that calcium is involved with, but most importantly, it’s a direct calcium channel antagonist… Magnesium is the primary calcium channel blocker.”
– “If I had to choose one supplement only, I would make it magnesium.“
second video: How Vitamin C Helps You Add Years to Your Life / Dr Thomas Levy Interview
– “A large number of diseases are caused by magnesium deficiency, and all diseases are made worse by magnesium deficiency. “
– “if you are on planet earth and alive today, you have low (suboptimal) magnesium levels. “
False diagnoses:
Blood tests are usually inconclusive, in particular: “serum blood levels do not represent body magnesium status.”
“Subclinical magnesium deficiency can exist despite the presentation of a normal status as defined within the current serum magnesium reference interval (0.75–0.95 mmol/L).” [25]
The body will always try to maintain a steady magnesium level in the serum, even in cases of severe deficiency, serum levels maybe stable or even elevated.
“Most cases of magnesium deficiency are undiagnosed. “ [26]
“Blood measurements can easily mask deficiency.” [27]
Effective tests:
Besides assessment of symptoms and reactions to supplementation, tests more conclusive than serum analysis are: either a hematocrit correlated whole blood analysis or a 24-hour magnesium loading urine test, these are almost never offered by general practitioners.
Supplementation/ dosage
The only known side effect of normal doses of 500 mg /day is initial loose stool or diarrhea. Paradoxically, this is usually an indication of Mg deficiency.
Dr. Russell Jaffe found: “those who are most susceptible to magnesium (react with diarrhoea) are most prone to have magnesium deficiency.” [28]
As mentioned above, all-in-one mineral and vitamin supplements usually contain only 10-15% of the RDA for magnesium. Health authorities claim this recommendation is based on the fact that there is sufficient magnesium in the normal diet, which might have been true in past centuries. Further, it is argued that if a 400 mg/day magnesium supplementation causes digestive problems, then the person must have had enough Mg in the diet already and the supplementation must have been overdosed.
Thus, some people believe they are allergic to magnesium. No one alive is allergic to magnesium, but rather deficient. As blood tests are inconclusive and Mg deficiency is almost universal, incrementally increasing slow supplementation over months is a good way to find out whether your health and mood can improve.
Further, it is sometimes claimed that only natural magnesium forms from foods can be absorbed. In reality, natural forms contained in foods include Mg sulphates, oxides and carbonates as in supplements.
Also ‘naturally present are magnesium glycinate, found in protein-rich foods like fish and nuts and magnesium malate found in fruits.’ Magnesium sulphate, commonly known as Epsom salts, is also found in some foods, including flour and cheese. [29]
As always, supplements do not replace a healthy, natural diet. Nowadays, most people need both. Magnesium rich foods include whole wheat, spinach, quinoa, almonds, cashews, peanuts, dark chocolate, black beans, edamame, avocado, tofu and yogurt.
Find the right form and dose that you can tolerate without problems and increase the dose incrementally. If you cannot tolerate 200 mg/day of any form without digestive problems after 3 months of increasing daily supplementation, see a doctor.
The magnesium forms which are generally best absorbed and well tolerated include magnesium bisglycinate (glycinate), followed by chloride, citrate, malate and lactate.
Dr. Berg recommends: don’t take magnesium oxide, it is absorbed only at a rate of 4%. This is also the most frequently sold form of Mg supplements. However, with normal gastric acid conditions, magnesium oxide is well absorbed (most people have a too high gastric pH, (not enough acidity). All supplement forms of magnesium other than oxide are usually effective with different people.
The upper limit of Mg was recently raised to 500 mg/day for an adult. [30]
Dr. Levy claims normal people cannot orally overdose magnesium, unless under extremely rare circumstances, for instance an 80+ year-old with severe constipation, where large oral doses of magnesium can accumulate in the intestines. Some therapists recommend 600- 1,000 mg per day. Dr. Markus Stark subscribes up to 3,000 mg/ day. [31]
500 mg /day means 500 mg of elemental magnesium. On the label it might say one capsule contains ’100 mg of magnesium as magnesium citrate’. Differently, 100 mg of magnesium citrate (as for instance in powder form) contains only ~11 mg of elemental magnesium.
Further common micronutrient deficiencies with the biggest health effects are vitamin C, vitamin D3, vitamin K, potassium and Omega-3 fatty acids (DHA and EPA).
—
Lithium and Magnesium
Lithium in high doses is used in psychiatric treatment (bipolar disorder). In small doses in drinking water, it is associated with lower suicide and lower mental illness rates. Also, lithium in drinking water is strongly correlated with magnesium and potassium in the same water, therefore it remains to be determined whether part of the beneficial effect of lithium-rich water is due to the higher magnesium and potassium intake.
“In drinking water, lithium and magnesium concentrations often show a positive correlation, meaning higher levels of one tend to be associated with higher levels of the other. This correlation is observed in both spring and bottled waters. The relationship is particularly strong in spring waters, with a high correlation coefficient (r=0.98, p<0.001) observed in one study.” [34]
– Magnesium and Covid
Long Covid/ post vac: “In conclusion, magnesium [deficiency] could be involved in the development of long COVID-19 syndrome and may aggravate symptoms or pre-existing conditions. Therefore, the evaluation and, if necessary, correction of magnesium is essential to achieve complete recovery in patients with long COVID-19 syndrome.” [32]
“Magnesium deficiency is intimately involved in the brain fog, fatigue, post-exertional malaise, headache, dizziness, myalgia and asthma of Long Covid or Post Acute Coronavirus Syndrome (PACS) also known as Post Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC).” [33]
[1] Patrick W. Chambers 2022: Long Covid, Short Magnesium; Department of Pathology, Torrance Memorial Medical Center, Torrance, CA, USA. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1108736 1108736-20220526-173329-3196.pdf
[2] Tarsitano MG, Quinzi F, et al 2024: Effects of magnesium supplementation on muscle soreness in different type of physical activities: a systematic review. J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 5;22(1):629. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-05434-x
[3] Quann, E. E., Fulgoni, V. L., & Auestad, N. (2016). Consuming the daily recommended amounts of dairy products would reduce the prevalence of inadequate micronutrient intakes in the United States: diet modelling study based on NHANES 2007–2010. South African Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 29(1), 32–41. https://doi.org/10.1080/16070658.2016.1215887
[4] Magnesium…the invisible deficiency – Campus Dining 2016 https://dining.nd.edu/whats-happening/news/magnesiumthe-invisible-deficiency/
[5] Orlova, S. et al 2022: Assessment of subclinical magnesium deficiency in pregnant women; https://doi.org/100.21518/2079-701X-2022-16-5-104-110
[6] Coman AE, et al. The Significance of Low Magnesium Levels in COVID-19 Patients. Medicina. 2023; 59(2):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020279
[7] Loh J.Y. et al 2025: Hypermagnesemia- and Hyperphosphatemia-Associated Cardiac Arrest after Injection of a Novel Magnesium-Based Bone Cement in Spinal Surgery, JAAOS: Global Research and Reviews, 9, 1, (2025). https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-24-00035
[8] Tarleton EK 2020; National Institutes of Health (NIH) (.gov) https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/7/2104
[9] Randomised controlled trial of physiotherapy compared with advice for low back pain BMJ 2004; 329 (Published 23 September 2004) https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38216.868808.7C
[10] pharmacytimes.com Study: Half of All Americans are Magnesium Deficient; Author(s): Sara Karlovitch Assistant Editor https://www.pharmacytimes.com/view/study-half-of-all-americans-are-magnesium-deficient
[11] https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/168894/nutrients
[12] USDA FoodData Central Food Details; Wheat flour, white, all-purpose, enriched, bleached; https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/168894/nutrients
[13] Statista: Glyphosate use in the United States from 1974 to 2014 (in 1,000 kilograms) https://www.statista.com/statistics/567162/glyphosate-use-in-the-united-states-in-kilograms/
[14] Workinger JL, Doyle RP, Bortz J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Magnesium Status. Nutrients. 2018; 10(9):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091202
[15] https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/food-details/168463/nutrients
[16] Walna, Barbara, et al : The impact of acid rain on calcium and magnesium status in typical soils of the Wielkopolski National Park, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 220, Issues 2–3, 1998, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(98)00240-X
[17] Cakmak, I. et al: 2009: Glyphosate reduced seed and leaf concentrations of calcium, manganese, magnesium, and iron in non-glyphosate resistant soybean,
European Journal of Agronomy, Volume 31, Issue 3, 2009, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2009.07.001.
[18] Worthington V. Nutritional quality of organic versus conventional fruits, vegetables, and grains. J Altern Complement Med. 2001 Apr;7(2):161-73. https://doi.org/10.1089/107555301750164244
[19] Ancient Minerals; Magnesium in the Diet: The Bad News about Magnesium Food Sources; https://www.ancient-minerals.com/transdermal-magnesium/dietary/
[20] Swaminathan R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin Biochem Rev. 2003 May;24(2):47-66. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1855626/
[21] Zhai Q, Narbad A, Chen W. Dietary strategies for the treatment of cadmium and lead toxicity. Nutrients. 2015 Jan 14;7(1):552-71. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7010552.
[22] NIH; Magnesium: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/
[23] Can Anti-Depressants Worsen Nutrient Depletion? Neuro Mend; 2024 https://blog.neuromendcenter.com/can-anti-depressants-worsen-nutrient-depletion
[24] Workinger JL, Doyle RP, Bortz J. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Magnesium Status. Nutrients. 2018; 10(9):1202. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091202
[25] Costello R.B, et al 2016: Perspective: The Case for an Evidence-Based Reference Interval for Serum Magnesium: The Time Has Come, Advances in Nutrition, Volume 7, Issue 6, 2016, https://doi.org/10.3945/an.116.012765.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2161831322007840)
[26] DiNicolantonio JJ, O’Keefe JH, Wilson W. Subclinical magnesium deficiency: a principal driver of cardiovascular disease and a public health crisis. Open Heart. 2018 Jan 13;5(1):e000668. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29387426/
[27] DiNicolantonio JJ, O’Keefe JH, Wilson W. Subclinical magnesium deficiency: a principal driver of cardiovascular disease and a public health crisis. Open Heart. 2018 Jan 13;5(1):e000668. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29387426/
[28] Video: loose stool from Magnesium? Here’s What to do. Dr. Susan E. Brown
[29] healthline.com ; 10 Types of Magnesium (and What to Use Each For) https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/magnesium-types#9-Magnesium-glycinate
[30] CRN raises safe upper level for magnesium supplements after evaluation https://www.nutritioninsight.com/news/crn-magnesium-ul-safety-supplements.html
[31] MAGNESIUM das Anti-Stress-Mineral Dr. rer. nat. Markus Stark erklärt https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bVhEOo3WfuU&t=357s
[32] Coman AE, et al. The Significance of Low Magnesium Levels in COVID-19 Patients. Medicina. 2023; 59(2):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020279
[33] Chambers, Patrick W. 2022: Long Covid, Short Magnesium; Department of Pathology, Torrance Memorial Medical Center, Torrance, CA, USA. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1108736 1108736-20220526-173329-3196.pdf
[34] Seidel, Ulrike & Baumhof, Elena et al (2019). Lithium‐Rich Mineral Water is a Highly Bioavailable Lithium Source for Human Consumption. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 63. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332852802_Lithium-Rich_Mineral_Water_is_a_Highly_Bioavailable_Lithium_Source_for_Human_Consumption
[sd1]Source






Leave a comment